Great
Red Spot
WIDER THAN OUR ENTIRE PLANET.
The spot, whose main cloud layer is likely ammonia, appears to be an area of upwelling, in which clouds billow up from below. We’re still unsure as to the exact chemistry responsible for the spot’s brick-red color, as many Jovian storms boast a similar shade. Some other storms are white, however.
On Earth, hurricanes grow over oceans and dissipate soon after making landfall. But because Jupiter lacks a surface that slows or confines storms, Jovian winds and hurricanes last for centuries – if not longer. Sometimes Jupiter’s storms merge, combining to form even larger oval features. Bigger storms like the Great Red Spot gobble up smaller neighbors.
Although calling features like the spot “storms” is an accurate way to describe them, they are technically termed anticyclones (cyclones whirl in the other direction). For scientists, a “storm” usually refers to turbulent updrafts of material, which appear less frequently and produce lightning.
-
actual title here
Category 5 Hurricane on Earth
SIZE200 Miles
WIND SPEED150 MPH
ROTATION SPEED3/HR
DURATION1-2 Days
The Great Red Spot
SIZE12000 Miles
WIND SPEED350 MPH
ROTATION SPEED1/6 Days
DURATION500 Years?
-
actual title here
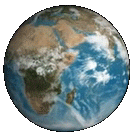

 The Great Red Spot is ~3 times the size of Earth.
The Great Red Spot is ~3 times the size of Earth. -
What is the Great Red Spot?


